Title
On January 20th, sixty corporations begin measuring the greenhouse gas emissions of their products and supply chains by road testing a new global framework that is part of the Greenhouse Gas Protocol Initiative.
Developed by the World Resources Institute (WRI) and the World Business Council for Sustainable Development (WBCSD), the two new GHG Protocol standards – the Product Life Cycle Accounting and Reporting Standard and the Scope 3 (Corporate Value Chain) Accounting and Reporting Standard – provide methods to account for emissions associated with individual products across their life-cycles and of corporations across their value chains.
Jonathan Lash, president of WRI, said, “We are encouraged by the overwhelming response from the private sector seeking to road test the new standards. There were more than 120 applications across a broad array of sectors and regions worldwide. The road testing will provide critical input in ensuring that the standards generate credible and meaningful data for business and government decision makers, while considering the practical challenges that businesses and programs will face during implementation.”
“Increasingly, companies are looking beyond their own boundaries and developing strategies to reduce GHG emissions in their supply chains and in the products they make and sell,” added Bjorn Stigson, president of WBCSD. “By taking a comprehensive approach to GHG measurement and management, businesses and policymakers can focus attention on the greatest opportunities to reduce emissions within the full value chain, leading to more sustainable decisions about the products companies buy, sell, and produce.”
While many companies have been measuring the emissions from their own operations and electricity use, the Scope 3 Standard will, for the first time, allow companies to look comprehensively at the impact of their corporate value chains, including outsourced activities, supplier manufacturing, and the use of the products they sell. Road testers of the Product Standard will measure the climate change impact of products ranging from magazines, food and jeans to computers, wind turbines and steel.
Ashley Crepiat, environmental footprint and economics manager for road-testing company Airbus, said, “Managing the transition towards a low-carbon economy is now a true concern for corporations. Airbus understands that beyond reducing its direct GHG emissions from its operations, evaluating emissions throughout the whole value chain is also a major challenge. By road testing GHG Protocol’s Scope 3 Accounting and Reporting Standard, we believe this will help establish harmonized international guidelines enabling a common and robust framework for Scope 3 accounting.”
Michael Kobori, Levi Strauss & Co.’s vice president of Social and Environmental Sustainability, said: “Levi Strauss & Co. is thrilled to be road-testing the GHG Protocol Product Life Cycle Accounting and Reporting Standard. If this method becomes widely accepted, it will enable us to better calculate and share the climate change impact of our products. Being able to credibly measure and communicate that product impact to consumers can unleash the power of the market to address climate change on a global scale.”
The draft standards were developed over the last year through a global, collaborative multi-stakeholder process, with participation from over 1,000 volunteer representatives from industry, government, academia and non-governmental organizations. The road testing process will provide real-world feedback to ensure the standards can be practically implemented by companies and organizations from a variety of sectors, sizes, and geographic areas around the world. The final standards are scheduled to be published in December 2010.
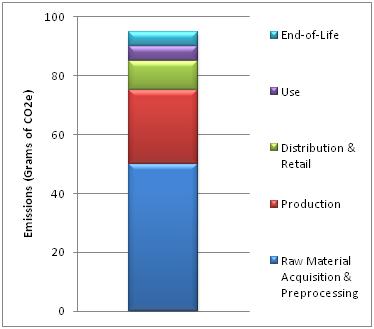
An example of GHG emissions across a product’s life cycle
Companies participating in the road testing represent 17 countries from every continent and more than 20 industry sectors. The companies include: 3M Company; Acer Inc.; Airbus S.A.S.; AkzoNobel; Alcan Packaging; Alcoa; Anvil Knitwear, Inc; Autodesk, Inc.; Baoshan Iron & Steel Co. Ltd.; BASF SE; Belkin International; Belron International; Bloomberg LP; BT Plc; CA, Inc.; Coca-Cola Erfrishungsgetränke AG; Colors Fruit SA (Pty) Ltd.; Deutsche Post DHL; DuPont; Eclipse Networks (Pty) Ltd.; Ecolab; The Estee Lauder Company; Ford Motor Company; General Electric; U.S. General Services Administration; Gold’n Plump Poultry LLC; Highways Agency (UK); Hydro Tasmania; IBM; IKEA; Italcementi Group; JohnsonDiversey, Inc.; Kraft Foods; Lenovo Corporation; Levi Strauss & Co.; Mitsubishi Chemical Corporation; National Grid; Natura Cosméticos; New Belgium Brewing Co.; Otarian; PepsiCo, Inc.; Pinchin Environmental Ltd.; PricewaterhouseCoopers (Hong Kong); Procter & Gamble Eurocor; Public Service Enterprise Group, Inc.; Rogers Communications, Inc.; SAP AG; SC Johnson; Shanghai Zidan Food Packaging & Printing Co., Ltd.; Shell International Petroleum Company Ltd; Suzano Pulp and Paper; Swire Beverages (Coca-Cola Bottling Partner); TAL Apparel Limited; Tech-Front (Shanghai) Computer Co., Ltd./Quanta Shanghai Manufacturing City; Tennant Company; Veolia Water; Verso Paper Corp.; VT Group Plc; Webcor Builders; Weyerhaeuser Company and WorldAutoSteel.